
 |
| You might also like: | Brown Things Color Book | Bactrian Camel Printout | Camel Quiz Worksheet | Bald Eagle | Oryx Printout | Today's featured page: Character Analysis Graphic Organizer Printouts |
| Go to Bactrian Camels | EnchantedLearning.com Arabian Camel or Dromedary | Animal Printouts Label Me! Printouts |

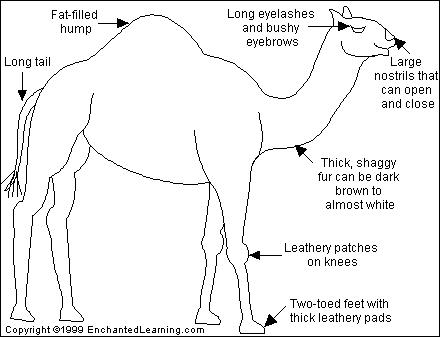
The Hump: The camel's hump contains fat (and NOT water). The camel can go without food and water for 3 to 4 days. It is well adapted to desert life.
Anatomy: Camels are very strong mammals with wide, padded feet. They have thick leathery pads on their knees and chest. Camels have nostrils that can open and close, protecting them from the desert environment. Bushy eyebrows and two rows of long eyelashes protect their eyes from sand. Their mouth is extremely tough, allowing camels to eat thorny desert plants. Camels are over 7 feet (2 m) tall at the hump and weigh in excess of 1,600 pounds (725 kg).
Diet: Camels are herbivores (plant-eaters). Most camels are domesticated and are fed by people; they eat dates, grass, wheat, and oats.
Classification:Class Mammalia (mammals), Order Artiodactyla, Suborder Tylopoda, Family Camelidae, Genus Camelus, Species C. dromedarius (dromedary camel) and C. bactrianus (Bactrian camel).
| Search the Enchanted Learning website for: |