
 |
| ZoomDinosaurs.com ALL ABOUT DINOSAURS! |
| What is a Dinosaur? | Dino Info Pages | Dinosaur Coloring Print-outs | Name That Dino | Biggest, Smallest, Oldest,... | Evolution of Dinosaurs | Dinos and Birds | Dino Myths |
| Supersaurus information printout | K-3 Supersaurus coloring page |
"Super Lizard"
|
ANATOMY
It's main food source was probably conifers. Secondary food sources may have included gingkos, seed ferns, cycads, bennettitaleans, ferns, club mosses, and horsetails.
HABITAT
LOCOMOTION
INTELLIGENCE
Supersaurus was a sauropod, whose intelligence (as measured by its relative brain to body weight, or EQ) was the among the lowest of the dinosaurs.
SUPERSAURUS is one of the longest land animals yet discovered. It was a long-necked, whip-tailed giant, measuring about 138 feet (42 m) long and 54 feet (16.5 m) tall, with a 39 foot (12 m) long neck. It may have had very limited vertical neck mobility. It may have weighed up to 55 tons; it was not the heaviest dinosaur. Its front legs were shorter than its back legs, and all the legs had elephant-like, five-toed feet. One toe on each foot had a thumb claw, probably for protection. It may have used its whip-like tail for protection.
BEHAVIOR
Supersaurus probably travelled in herds and may have migrated when they depleted their local food supply. Supersaurus may have hatched from eggs, like other sauropods. Sauropod eggs have been found in a linear pattern and not in nests; presumably the eggs were laid as the animal was walking. It is thought that sauropods did not take care of their eggs. Sauropod life spans may have been on the order of 100 years.
WHY WAS SUPERSAURUS' NECK SO LONG?
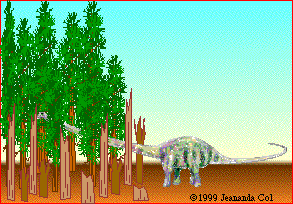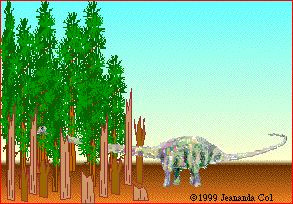 Supersaurus held its neck more or less horizontally (parallel to the ground). The long neck may have been used to poke into forests to get foliage that was otherwise unavailable to the huge, lumbering varieties of sauropods who could not venture into forests because of their size. Alternatively, the long neck may have enabled this sauropod to eat soft pteridophytes (horsetails, club mosses, and ferns). These soft-leaved plants live in wet areas, where sauropods couldn't venture, but perhaps the sauropod could stand on firm ground and browse in wetlands.
Supersaurus held its neck more or less horizontally (parallel to the ground). The long neck may have been used to poke into forests to get foliage that was otherwise unavailable to the huge, lumbering varieties of sauropods who could not venture into forests because of their size. Alternatively, the long neck may have enabled this sauropod to eat soft pteridophytes (horsetails, club mosses, and ferns). These soft-leaved plants live in wet areas, where sauropods couldn't venture, but perhaps the sauropod could stand on firm ground and browse in wetlands.
DIET
Supersaurus was an herbivore (it ate only plants). It must have eaten a tremendous amount of plant material each day to sustain itself. It swallowed leaves whole, without chewing them, and may have had gastroliths (stomach stones) in its stomach to help digest this tough plant material. It had blunt teeth, useful for stripping foliage.
Given Supersaurus obvious need for an abundant source of plants to eat, it must have lived in relatively lush forest habitats. Herds of Supersaurus may have migrated to rich feeding grounds.
Supersaurus moved slowly on four legs (as determined from fossilized tracks and its leg length and estimated mass).
It used to be thought that the sauropods (like Supersaurus, Brachiosaurus and Apatosaurus) and Stegosaurus had a second brain. Paleontologists now think that what they thought was a second brain was just an enlargement in the spinal cord in the hip area. This enlargement was larger than the animal's tiny brain.
FOSSILS
The first Supersaurus fossil was found in western Colorado, USA, by paleontologist James A. Jensen in 1972, and was named in 1985. It is only known from an incomplete fossil which includes two shoulder blades 8 feet (2.4 m) long, ribs 10 feet (3 m) long, neck vertebrae 4.5 feet (1.4 m) long, and a pelvis 6 feet (1.8 m ) wide.
CLASSIFICATION
Supersaurus was a huge herbivorous dinosaur that belonged to the:
SUPERSAURUS PRINTOUTS
Supersaurus information printout
Print out a K-3 Supersaurus page to color!
 (and Other Prehistoric Creatures) |
Enchanted Learning®
Over 35,000 Web Pages
Sample Pages for Prospective Subscribers, or click below
|
Overview of Site What's New Enchanted Learning Home Monthly Activity Calendar Books to Print Site Index K-3 Crafts K-3 Themes Little Explorers Picture dictionary PreK/K Activities Rebus Rhymes Stories Writing Cloze Activities Essay Topics Newspaper Writing Activities Parts of Speech Fiction The Test of Time
|
Biology Animal Printouts Biology Label Printouts Biomes Birds Butterflies Dinosaurs Food Chain Human Anatomy Mammals Plants Rainforests Sharks Whales Physical Sciences: K-12 Astronomy The Earth Geology Hurricanes Landforms Oceans Tsunami Volcano |
Languages Dutch French German Italian Japanese (Romaji) Portuguese Spanish Swedish Geography/History Explorers Flags Geography Inventors US History Other Topics Art and Artists Calendars College Finder Crafts Graphic Organizers Label Me! Printouts Math Music Word Wheels |
Click to read our Privacy Policy
| Search the Enchanted Learning website for: |