 |
BRAIN CELLS |
 |
BRAIN CELLS
The brain and spinal cord are made up of living cells, neurons and glial cells. Neurons send and receive electro-chemical signals to and from the brain and nervous system. There are about 100 billion neurons in the brain. There are many more glial cells; they provide support functions for the neurons, and are far more numerous than neurons.
There are many type of neurons. They vary in size from 4 microns (.004 mm) to 100 microns (.01 mm) in diameter. Their length varies from a fraction of an inch to several feet.
| NEURON |
|
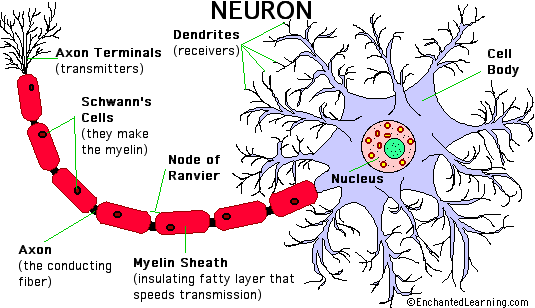
Neurons are nerve cells that transmit nerve signals to and from the brain at up to 200 mph (check this). The neuron consists of a cell body (or soma) with branching dendrites (signal receivers) and a projection called an axon, which conduct the nerve signal. At the other end of the axon the axon terminals transmit the electro-chemical signal across a synapse (the gap between the axon terminal and the receiving cell). |
USE THIS,
AND THIS
The axon, a long extension composed of. . Bundles of axons are known as nerves or, within the CNS, as nerve tracts or pathways.
Myelin coats and insulates the axon (except for periodic breaks called Nodes of Ranvier), increasing transmission speed along the axon. Myelin is manufactured by Schwann's Cells, and consists of 70-80% lipis (fat) and 20-30% protein.
The cell body (soma) contains the neuron's nucleus (With DNA and typical organelles), . Dendrites branch from the cell body
A typical neuron has about 1,000 to 10,000 synapses (that is, it communicates with 1,000-10,000 other neurons, muscles cells, glands, etc.).
DIFFERENT TYPES OF NEURONS
There are different types of neurons. They all carry electro-chemical nerve signals, but differ in structure (the number of processes, or axons, eminating from the cell body) and are found in different parts of the body.
- Sensory neurons or Bipolar neurons carry messages from the body's sense receptors (eyes, ears, etc.) to the CNS. These neurons have two processes. Sensory neuron account for 0.9% of all neurons. (examples are retinal cells, olfactory epithelium cells)
- Motoneurons or Multipolar neurons carry signals from the CNS muscles and glands. These neurons have many processes originating from the cell body. Motoneurons account for 9% of all neurons. (examples are spinal motor neurons, pyramidal neurons, Purkinje cells)
- Interneurons or Pseudopolare (Spelling) cells form all the neural wiring within the CNS. These have two axons (instead of an axon and a dendrite). One axon communicates with the spinal cord; one with either the skin or muscle. These neurons have two processes. Sensory neuron account for 90% of all neurons. (examples are dorsal root ganglia cells)
THE ELECTROCHEMICAL SIGNAL
action potential
LIFE SPAN OF NEURONS
Unlike most other cells, neurons cannot regrow after damage. Fortunately, there are about 100 billion neurons in the brain.
GLIAL CELLS
Glial cells are nerve cells that don't carry nerve impulses. The various glial (meaning "glue") cells perform a many support functions for the neuropns, including: digestion of parts of dead neurons, manufacturing myelin, providing physical and nutritional support, and more. There are 10-50 times more glial cells than there are neurons. Types of glial cells include Schwann's Cells, SSatellite Cells, Microglia, Oligodendroglia, Astroglia. (Neuroglia (meaning "nerve glue") are the another type of brain cell. These cells guide neurons during fetal development. ????)
Enchanted Learning®
Over 35,000 Web Pages
Sample Pages for Prospective Subscribers, or click below
Click to read our Privacy Policy
Enchanted Learning Search
|
Search the Enchanted Learning website for:
|
Advertisement.
Advertisement.
Copyright ©1996-97 Enchanted Learning Software