Advertisement.
EnchantedLearning.com is a user-supported site.
As a bonus, site members have access to a banner-ad-free version of the site, with print-friendly pages.
Click here to learn more.
(Already a member? Click here.)
Questions about Particular Dinosaurs C-D
(in alphabetical order)
Q: How do Camarasaurus defend themselves?
from Chris, Chicago, IL, USA; October 6, 1998
A: Although it was small for a sauropod, Camarasaurus was still huge (over 60 feet or 18 m long). Its size was its primary protection from predators. Also, it had a long, sharp claw on its inner toe. Its tail may have also been used to swat away predators, although this is uncertain. For an information sheet on Camarasaurus, click here.
Q:Why is the Camarasaurus dinosaur called the chambered lizard? What does chambered mean?
from Kenny D., Pullman, Washington, USA; Nov. 3, 1997
A: Chambered refers to the holes in its vertebrae. The holes made the bones more light-weight while retaining structural strength.
Q: What specific stuff did the Camptosaurus eat?
from Jason L., Sparta, NJ, USA; November 27, 1998
A: Unless fossilized stomach contents or fossilized dung are found (and these are VERY rare), a dinosaur's exact diet is unknown. Its teeth do tell you something about its diet, and Camptosaurus was a plant eater. For more information on Camptosaurus, click here.
Q: Can you please post information on Camptosaurus? Also, I want to know what the climate is like during the Late Jurassic Period. Does Camptosaurus live in herds or alone or packs? Thank You!!!
from Kate, El Paso, TX, USA; April 28, 1998
A: Camptosaurus (meaning "bent lizard") was a plant-eater from the late Jurassic period (about 156 to 145 million years ago) that looked a lot like Iguanodon. It was a heavy ornithischian dinosaur that was about 16-23 feet (5-7 m) long and 3-4 feet (1 m) high at the hips. It had a long snout, much longer legs than arms, had four-toed feet and hoofed fingers and toes. It could walk on two or four legs, it probably went on all four to graze for low-lying plants. Its fossils have been found in North American and Europe. It was first found in Utah, USA by the dinosaur collector Earl Douglass and named by paleontologist Othniel C. Marsh in 1885. Many fossils of Camptosaurus have been found, in different stages of development. Camptosaurus may have lived in herds.
The climate during the late Jurassic was hot and moist. For information on the Jurassic period, click here.
Q: what was the height of a camptosaurus? also what type of habitat did it live in?
from sean e.; September 16, 1997
A:Camptosaurus (meaning bent lizard) was about 7 feet (2 m) tall and 17 feet long (5 m). This herbivore from the late Jurassic had a horny beak and small hooves on its hands and feet. It could walk on two feet, but perhaps walked on all four when grazing (as suggested by the hooves). It has been found in Wyoming, Utah, and Colorado in the western US.
Q:Please send me information about Camptosaurus. Thanks
from Alex, Sugar Land, TX, USA; Feb. 11, 1998
A: Camptosaurus (meaning "flexible or bent lizard") was a large, bipedal, Jurassic herbivore (plant-eater) with hundreds of teeth and a horny beak. Hooves on its fingers (it had five fingers on each hand, each with a hoof) indicate that it probably walked on all fours some of the time, probably when grazing. Its legs were much longer than its arms.
There are a lot of species of Camptosaurus, ranging from the size of a turkey to about 20 feet long and 7 feet tall. Fossils have been found in Europe and North America. Camptosaurus was an ornithopod ( a bipedal, herbivorous ornithischian dinosaur).
Q: I am in second grade and need to find out whatever I can about the Camptosaurus dinosaur. I know it lived during the late Jurassic period. Can you help me?
from Vinny, New Hope, PA, USA; March 29, 1998
A: Camptosaurus was a plant-eater that was up to 20 feet (6 m) long. It had a long snout and a horny beak. It walked on two legs, but probably went on all fours to graze for low-lying plants. It had strong legs with three-hoofed toes. Its arms were smaller than its legs and they had five fingers with hoof-like nails.
It was an early ornithopod; it was closely related to the family Iguanodontidae (which included Iguanodon). It lived during the late Jurassic and was a very common dinosaur. There were many species of Camptosaurus. Fossils have been found in North America and Europe. Camptosaurus means "bent lizard."
Q:I am doing a very large report on the dinosaur Camptosaur I need to know what kind of area that they lived in like the desert or a forest I as need to know how tall they get, What colors they are and what is their scientific name.
from L.P., Duluth, MN, USA; Feb. 17, 1998
A: There were many species of Camptosaurus (which means "bent lizard"). They lived in what is now North America and Europe during the Jurassic, a time of warm, tropical weather. It grew to be about 21 feet (6.5 m) long. No one knows what colors any of the dinosaurs were. Dinosaurs' scientific names are the same as their common names.
Q: How fast did camptosaurus run? How did it move? What did it do to protect itself from enemies?
from Abraham R., Sharon, MA, USA; June 9, 1998
A: Camptosaurus could walk on two or four legs. It was a bulky dinosaur and probably not an incredibly fast runner but have been able to go about 20-30 mph (32-48 kph) in short bursts. It had almost no protection from predators (like Allosaurus); it had no horns, no armor, no sharp teeth, no plates, and hooves, not claws. For more information on Camptosaurus, click here.
Q: Is this dino the most recent dino Carcharodontosaurus if not what one is? What are some facts about the most recent dino?
from Brandon H, Sheridan, WY, USA; October 5, 1998
A: Carcharodontosaurus was first found in 1931 by Ernst Stromer von Reichenbach. In 1996, Paul Serano and his team found another Carcharodontosaurus in North Africa, even larger than the older specimen. For more information on Carcharodontosaurus, click here.
Many other dinosaurs have been found in the last few years. Some very recent finds include Scipionyx, Protarchaeopteryx, Caudipteryx, Unenlagia, Giganotosaurus, Sinosauropteryx, and many others. Also see the section on Dino News for updates.
Q: i AM LOOKING FOR INFORMATION ON A DINOSAUR CALLED A CHICKENDONOSAURUS. IS THERE SUCH A DINOSAUR?? THE SPELLING MIGHT NOT BE CORRECT. THANK YOU. SUZANNE
from Suzanne C., Los Gatos, CA, USA; December 4, 1998
A: Your nephew might be reffering to Carcharodontosaurus (I hope!). It was a huge meat-eater, even bigger than T. rex. There's an information sheet about Carcharodontosaurus here.
Q:looking for info on the carnosaurus. Thanks.
from Sheena, Cornwall, Ontario, Canada; Nov. 6, 1997
A: Carnosauria (also referred to as Allosauria, meaning "different lizard") were huge predators, and a type of theropod (they were meat eaters who walked on two legs, had large tails, sharp teeth, and large heads). They lived through the late Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The Carnosaurs include Allosaurids and their relatives, including Monolophosaurus, Cryolophosaurus, Allosaurus, Giganotosaurus, the enormous Carcharodontosaurus, and others.
Q: Are there any dinosaurs called Ceratosaurus?
from Jolis G., Kota kinabalu, Sabah, Malaysia; November 28, 1998
A: Yes, check out the entry in the Dinosaur Dictionary.
Q: Can you tell me about the "Chasmosaurus" was he a friendly dinosaur? Thank You, P.J.
from P.J., Lindenhurst, Illinois, USA; November 16, 1998
A: Chasmosaurus was a ceratopsian, a plant-eating dinosaur built like a rhinoceros. For an information sheet on Chasmosaurus, click here. I doubt that any dinosaurs were friendly.
Q:Where can I find more info about Coelophysis?
from Laura, Ponte Verde, Florida, USA; Nov. 28, 1997
A: Coelophysis (meaning "hollow form") was an early bipedal predator (a theropod) that lived in the late Triassic. It was relatively small, about 10 feet long (3 m) and weighed about 100 pounds (45 kg). It had long toothed jaws, a long neck, short three-fingered hands, and strong legs with three toes and a claw. Fossils have been found in New Mexico, USA and the eastern USA.
Q: i am doing a report on coelophysis. do you have any info i can use?
from bb, ferndale, washington, USA; October 12, 1998
A: For an information sheet on Coelophysis, click here.
Q: What fossils does a Coelophysis have?
from UDONIS H., Gainesville, Florida, USA; October 13, 1998
A: Several hundred Coelophysis fossil skeletons have been found in Arizona, New Mexico, and perhaps Utah. Adults and juveniles have been found. For an information sheet on Coelophysis, click here.
Q: I am doing a report on the Coelophysis and I cant find any info on it can you help me?
from Laura, Bensenville, Ill, USA; April 25, 1998
A: Coelophysis (meaning "hollow form") was a small, bipedal (two legged) meat-eater from the late Triassic period. This early theropod dinosaur was about 9 feet (2.8 m) long, lots of small, sharp teeth in long jaws, a long neck, long tail, long, thin legs, short arms, three-fingered hands with claws, and light, hollow bones (hence its name). Coelophysis was originally found in New Mexico in the 1870's by David Baldwin and named in 1889 by Edward Drinker Cope.
The status of this genus has been confused and controversial; the dinosaurs Coelophysis bauri and Rioarribasaurus colberti (New Mexico's state fossil) may or may not be different genera, different species, or just different animals in the same species. I think that the name Coelophysis has been determined to be the species type.
Q: I am working on a school project and need to find some information on a dinosaur named Coelurus. Can you help me locate some information on this dinosaurs. I am most interested in knowing how tall it was and our teacher asked us to find an interesting fact about this dinosaur. Thank you.
from Mike B., NC, USA; September 24, 1998
A: Coelurus (meaning "hollow") is a poorly known genus. It was perhaps a bipedal theropod dinosaur 6 feet (1.8 m) long. It was a carnivore that lived during the late Jurassic period, about 156 to 145 million years ago. Its bones were hollow and lightweight, so Coelurus was probably light and fast. Its fossils were found in Wyoming. Coelurus was named by Othniel C. Marsh in 1879.
Q: What is the scientific name of the Compsognathus?
from Lauren K, Toledo, Ohio, USA; October 19, 1998
A: Compsognathus is the scientific name of that genus. The dinosaurs are the only animals that are commonly known by their scientific names.
Q: How or what caused the Compsognathus to become extinct?
from art s, los angeles, la, USA; November 12, 1998
A: Compsognathus lived in the late Jurassic period, about 155 to 145 million years ago. There was an minor extinction about the time when Compsognathus died out. For more information on Compsognathus, click here.
 Q: Do you have any infomation on the compsognathus? Was the term dinosaur invented by Sir Richard Owen? what is the name of the second largest dinosaur? Also what is the name of the second smallest dinosaur?
Q: Do you have any infomation on the compsognathus? Was the term dinosaur invented by Sir Richard Owen? what is the name of the second largest dinosaur? Also what is the name of the second smallest dinosaur?
from Trevor, Port Charlotte, FL, USA; April 15, 1998
A: Yes, for an information sheet on Compsognathus, click here. Yes, Sir Richard Owen coined the term dinosaur in 1842. For a lot of extreme dinosaurs, click here.
Q: What is the Corythosaurus's social Behavior?
from Tim I., Greeley, Colorado, USA; December 2, 1998
A: For information on Corythosaurus, click here.
Q:Will you give me information about the Corythosaurus dinosaur?
from Jacob D., Dumas, TX, USA; Jan. 5, 1998
 A: Corythosaurus (meaning "helmet lizard") was a duck-billed dinosaur from the late Cretaceous period (70-95 million years ago). It had a helmet-like crest on its narrow head. This crest may have been used to make sound as it contained a system of tubes that went from the throat to to the nose. It walked on two legs and was a plant eater. It was about 30 feet (9 m) long and weighed about 2-3 tons. Fossils have been found in western North America, including a nearly complete skeleton from Alberta Canada.
A: Corythosaurus (meaning "helmet lizard") was a duck-billed dinosaur from the late Cretaceous period (70-95 million years ago). It had a helmet-like crest on its narrow head. This crest may have been used to make sound as it contained a system of tubes that went from the throat to to the nose. It walked on two legs and was a plant eater. It was about 30 feet (9 m) long and weighed about 2-3 tons. Fossils have been found in western North America, including a nearly complete skeleton from Alberta Canada.
Q: My second graders are studying dinosaurs. We can't seem to find enough information on the Corythosaurus. We need to know the height, weight, description and how many years ago it lived. Thanks for your help!
from Betsey W., Bordentown, NJ, USA; April 3, 1998
A: Corythosaurus was a large, plant-eating, duck-billed dinosaur (family Hadrosauridae). It was about 30 feet (9 m) long and may have weighed up to 5 tons. It had a hollow, bony crest on top of its long head in the shape of a helmet flattened on the sides (Corythosaurus means "helmet lizard"). The crest may have been used to make sounds, as a cooling device, for courtship rituals, and/or as a sense-of-smell enhancer. Males had larger crests than females and juveniles. It had a toothless beak and hundreds of cheek teeth that it used to grind up its food. It walked on two legs, had shorter arms, and a long, heavy tail. It was probably a fast runner - this was its only means of protection from predators like T. rex.
Corythosaurus lived in herds during the late Cretaceous period, going extinct 65 million years ago in the K-T mass extinction. It ate pine needles, seeds, fruit, twigs, and magnolia leaves. Fossils have been found in Alberta, Canada and Montana, USA. Click here to see an information sheet of Corythosaurus.
Q: Do you have any new information concerning the dinosaur called "Deinocheiros"? Was it a carnivore? Did it belong to the raptors or dromaeoaurs or any other carnivors of this normally small individuals? Deinocheiros had extraordinary big arms, and nothing more was found so far, am I right? Is there any progress in science
concerning this species? It would be nice to hear from you.
Thanx a lot and best wishes. Axel
from schuch, nürnberg, bavaria, germany; March 12, 1998
A: Deinocheirus (meaning "terrible hand") was a bipedal carnivore (meat-eater) from the late Cretaceous period. It is classified as a saurischian (lizard-hipped dinosaurs), a theropod, a coelurosaur, and an ornithomimid (bird mimic). It was probably not a dromeosaur (the "raptors," another subgroup of the coelurosaurs). Note: the classification of the dinosaurs is changing all the time, especially with animals like Deinocheirus, whose fossils are terribly incomplete.
As you wrote, only the arms, hands, and claws of Deinocheirus have been found (in the Gobi desert of Mongolia in 1965). The arms are 8 feet (2.4 m) long and have three fingers with long, hook-like claws, 8-12 inches (20-30 cm) long. The hands alone were 2 feet (60 cm) long. Deinocheirus was probably one of the most deadly dinosaurs of the late Cretaceous period. It may have been larger that T. rex.
Q: How do you pronounce deinonychus
from J.D., Cheyenne, Wyoming, USA; November 14, 1998
A: die-NON-ih-kus (emphasis on the NON).
Q:When did the Deinonychus become extinct?
from ???; Dec. 2, 1997
 A: Deinonychus (meaning "terrible claw") lived and died during the Cretaceous period, from about 110 to 100 million years ago.
A: Deinonychus (meaning "terrible claw") lived and died during the Cretaceous period, from about 110 to 100 million years ago.
Q:What dinosaurs lived with Deinonychus?
from Andrew, Los Alamitos, CA, USA; Dec. 25, 1997
 A: Deinonychus was a carnovore, lightly built, fast-moving, agile, bipedal (walking on two legs), bird-like dinosaur. It had a curved, flexible neck and a big head with sharp, serrated teeth in very powerful jaws. Deinonychus lived in the Cretaceous period, about 110 to 100 million years ago.
A: Deinonychus was a carnovore, lightly built, fast-moving, agile, bipedal (walking on two legs), bird-like dinosaur. It had a curved, flexible neck and a big head with sharp, serrated teeth in very powerful jaws. Deinonychus lived in the Cretaceous period, about 110 to 100 million years ago.
Among the contemporaries of Deinonychus were Spinosaurus (a carnasaur), Archaeornithomimus (another swift, bird-like Theropod), Sauroplites (an Ankylosaurid, a plated herbivore), Sauropelta (a Nodosaur, another armored herbivore), Probactrosaurus (an Iguanodontid) Titanosaurs (sauropods), and Tenontosaurus (a hypsilophodontid).
Q:Where did Deinonychus live?
from Diego G., Ridgewood, NY, USA; Feb. 1, 1998
 A: Deinonychus fossils have been found in Montana, USA.
A: Deinonychus fossils have been found in Montana, USA.
Q: I am doing some research on a dinosaur called Dicraeosaurus.I have found info about him on this site before but I forget where?It is not in the Dino Dicionary.So where is it?
from Kevin M., West Milford, NJ, USA; December 6, 1998
A: I've added Dicraeosaurus to the Dinosaur Dictionary.
Q:I need some information about Dilophosaurus. How tall was he? Did he have any enemies? What other meat eaters were living in the early Jurassic period?
from Daniel, Boone, IA, USA; Feb. 17, 1998
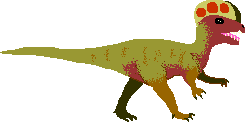 A: Dilophosaurus (meaning "two-crested lizard") was a speedy bipedal (walked on two legs) meat-eater from the late Triassic and early Jurassic periods. It was a theropod about 20 feet (6 m) long. It had short arms with three-fingered hands and strong legs with four-toed feet (one toe was a dew-claw). Both fingers and toes had claws. Fossils have been founds in Arizona, USA. Among its contemporaries in North America during the late Triassic and early Jurassic, all smaller than Dilophosaurus, were:
A: Dilophosaurus (meaning "two-crested lizard") was a speedy bipedal (walked on two legs) meat-eater from the late Triassic and early Jurassic periods. It was a theropod about 20 feet (6 m) long. It had short arms with three-fingered hands and strong legs with four-toed feet (one toe was a dew-claw). Both fingers and toes had claws. Fossils have been founds in Arizona, USA. Among its contemporaries in North America during the late Triassic and early Jurassic, all smaller than Dilophosaurus, were:
- the meat-eaters: Coelophysis(about 10 feet long), Syntarsus, and Segisaurus
- the omnivores: Massopondylus, and Anchisaurus
- the plant-eaters: Scutellosaurus, and Ammosaurus.
Although all of Dilophosaurus' contemporary carnivores were smaller than it, a pack of Coelophysis may have been able to kill a Dilophosaurus.
 Q: Did Dilophosaurus really spit poison out of its mouth at enemies?
Q: Did Dilophosaurus really spit poison out of its mouth at enemies?
from Casey W.; August 14, 1998
A: Only in the movies. For more information on Dilophosaurus, click here.
Q: I was looking for some information on the Dilophosaurus. But I can barely find a page of info if you have some please send it to me.
from Ben S., Chesapeake, Virginia, USA; May 11, 1998
 A: For an information sheet on Dilophosaurus, click here.
A: For an information sheet on Dilophosaurus, click here.
 Q: In the movie Jurassic Park, the Dilophosaurus spit poison. However, I haven't discovered anything about this in research I have done. Did Dilophosaurs really spit poison or did Jurassic Park writers make up this "fact"?
Q: In the movie Jurassic Park, the Dilophosaurus spit poison. However, I haven't discovered anything about this in research I have done. Did Dilophosaurs really spit poison or did Jurassic Park writers make up this "fact"?
from J. C., Baltimore, MD, USA; March 25, 1998
A: There is no fossil evidence that Dilophosaurus spat poison (or anything else). For an information sheet on Dilophosaurus, click here.
Q: How long,tall,and wide was the tallest,longest,and widest Diplodocus? I need to know how big the Diplodocus is could you give me a picture of their size against a human?
from ??; November 30, 1998
A: See the information sheet on Diplodocus for its length.
Q: What is a Diplodocus?
from Tara G., West Hamlin, W.V., USA; December 7, 1998
A: A large, plant-eating dinosaur. For more information, click here.
Q:I just want to know some information on Diplodocus.
I would appreciate if you can help me to answer the following
questions:
1) their habitat
2) social behaviour
3) where they lived and type of rock in which fossils are formed.
from Benson T., Aurora, Ontario, Canada; Feb. 22, 1998
 A:1) Diplodocus, a large late-Jurassic sauropod, was an herbivore, eating Cycads and other plant material. During the Jurassic, the Earth had a very warm, humid climate. Diplodocus must have lived in an area rich in plant life in order to sustain its bulk.
A:1) Diplodocus, a large late-Jurassic sauropod, was an herbivore, eating Cycads and other plant material. During the Jurassic, the Earth had a very warm, humid climate. Diplodocus must have lived in an area rich in plant life in order to sustain its bulk.
2) I can't find information on Diplodocus social behavior, but a lot of sauropods travelled in herds (as evidenced by fossilized trackways), and hatched from eggs.
3) Fossils usually form in sedimentary rock; click here to see pages on fossils.
Click here for an information page on Diplodocus
Q:what dinosaurs lived in the same period that the diplodocus lived in?
from mommy daddy, nj, nj, USA; Dec. 3, 1997
A: Diplodocus lived in the late Jurassic period, from 155-145 million years ago. The late Jurassic was the time of the enormous sauropods, including Camarasaurus, Apatosaurus, and Brachiosaurus. Also present were Stegosaurus, Tuojiangosaurus, Allosaurus, Coelurosaur, and many others.
Q:I am doing my science project on Diplodocus and I am having trouble finding the following: where they lived according to the continental formation and do they have and adaptations & special features? thanks
from Mark, Richmond Hill, Ontario, CA; Feb. 22, 1998
and from Mark, Scarbrough, Ontario, CA; Feb. 23, 1998
 A: Many Diplodocus fossils have been found in the Rocky Mountains of western North America (in Colorado, Montana, Utah, and Wyoming). For its special features, notably its hollow, anvil-shaped vertebrae, click here for an information sheet on Diplodocus
A: Many Diplodocus fossils have been found in the Rocky Mountains of western North America (in Colorado, Montana, Utah, and Wyoming). For its special features, notably its hollow, anvil-shaped vertebrae, click here for an information sheet on Diplodocus
Q: I am doing a project on Dromaeosaurus dinosaurs and can only seem to find info on Velociraptors. What are the differences between the two and where can I find a picture of the Dromaeosaurus?
from Josh R., Crofton, Maryland, USA; Feb. 28, 1998
A: Dromaeosaurus and Velociraptor were very similar. They were both from the family Dromaeosauridae, a family of terrifying predators from the Cretaceous period. This family was the smartest of all dinosaurs and was also speedy, large-headed, clawed, and may have hunted in packs. They had sharp teeth, a large, sickle-shaped claw on one toe, and clawed hands. The family includes Deinonychus 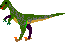 , Velociraptor, Dromaeosaurus, Saurornitholestes, etc.). Velociraptor and Dromaeosaurus were about the same size and both lived during the late Cretaceous.
, Velociraptor, Dromaeosaurus, Saurornitholestes, etc.). Velociraptor and Dromaeosaurus were about the same size and both lived during the late Cretaceous.
As for differences between the two, Velociraptor had a longer, flatter snout and a slightly smaller sickle-shaped toe claw than the other Dromaeosaurids (including Dromaeosaurus). Also, Velociraptor has been found in Asia while Dromaeosaurus has been found in North America. Dromaeosaurus is only known from incomplete fossils, while many Velociraptor fossils have found.
Q: I have two questions,1)How many species were there?
2)Do you have any info on the dryosaurus?
from Jonathan A., Hillsborough, N.B., CA; March 5, 1998
A: 1) There are about 330 described dinosaur genuses and many more species, but there are many, many more that have not been discovered (or may not even have been preserved in the fossil record).
 2) Dryosaurus (meaning "oak lizard") was a fast moving, agile, herbivorous (plant eater) dinosaur. It was about 10 feet (3 m) long and 4.5 feet (1.4 m) tall. It had large eyes, long, thin legs with three toes, shorter arms with five long fingers, a horny beak and cheek teeth. It may have stored food in its cheeks. It had a long neck and a stiff tail used for balance. It laid eggs and may have travelled in herds. There may have been some parental care for the young.
2) Dryosaurus (meaning "oak lizard") was a fast moving, agile, herbivorous (plant eater) dinosaur. It was about 10 feet (3 m) long and 4.5 feet (1.4 m) tall. It had large eyes, long, thin legs with three toes, shorter arms with five long fingers, a horny beak and cheek teeth. It may have stored food in its cheeks. It had a long neck and a stiff tail used for balance. It laid eggs and may have travelled in herds. There may have been some parental care for the young.
Dryosaurus lived during the late Jurassic to early Cretaceous periods. Its contemporaries were Apatosaurus, Diplodocus, Brachiosaurus, Coelurus, Allosaurus, Stegosaurus, and Ceratosaurus.
It is a Hypsilophodontid (which includes the smaller Hypsilophodon, Othnielia, Tenontosaurus, Parkosaurus, and Thescelosaurus). Fossils have been found in western North America and Africa.
Q: what is the name of the duck billed dinosaur?
from Tiffany S., woodhaven, ny, USA; August 18, 1998
A: There were a lot of different duck-billed dinosaurs, the Hadrosaurids, which included the family HADROSAURINAE and LAMBEOSAURINAE. They were all plant-eaters that had a toothless beak and many cheek teeth.
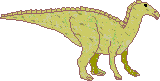 The Hadrosaurinae included species like Anatotitan, Edmontosaurus, Hadrosaurus, Kritosaurus, Maiasaura, Trachodon, Tsintaosaurus, and many others.
The Hadrosaurinae included species like Anatotitan, Edmontosaurus, Hadrosaurus, Kritosaurus, Maiasaura, Trachodon, Tsintaosaurus, and many others.
 Lambeosaurinae were duck-bills with hollow, bony head crests and included species like Lambeosaurus, Bactrosaurus, Corythosaurus, Jaxartosaurus, Parasaurolophus, and many others.
Lambeosaurinae were duck-bills with hollow, bony head crests and included species like Lambeosaurus, Bactrosaurus, Corythosaurus, Jaxartosaurus, Parasaurolophus, and many others.
Return to the top of the page.
Enchanted Learning®
Over 35,000 Web Pages
Sample Pages for Prospective Subscribers, or click below
Click to read our Privacy Policy
Enchanted Learning Search
|
Search the Enchanted Learning website for:
|
Advertisement.
Advertisement.
Copyright ©1997-2018
EnchantedLearning.com ------ How to cite a web page

