
 |
Volcano Info |
Volcano Dictionary |
Volcano Activities and Printouts |
|
| Types of Volcanoes | The Ring of Fire | ||
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z |
| Paleozoic era The Paleozoic era (540 to 245 million years ago) saw an explosion of new life forms. It ended with the largest mass extinction in history and was followed by the Mesozoic Era. |
 Pangaea Pangaea was a supercontinent consisting of all of Earth's land masses. It existed during the Permian and Jurassic period. It began breaking up during the Jurassic period, forming continents Gondwanaland and Laurasia, separated by the Tethys Sea. |
Pele's hair Pele's hair is a Hawaiian term for natural spun glass that can be as much as 2 m long. It is formed from the fountaining of fluid basaltic lava, cascading lava falls, or from turbulent lava flows. |
period The period is the basic unit of geological time in which a single type of rock system is formed, lasting tens of millions of years. |
Permian period Also known as "The Age of Amphibians" (280 to 245 million years ago), this is the time when Pangaea formed and Earth's atmosphere was oxygenated to modern levels. It ended with the largest mass extinction and was followed by the Mesozoic Era. Ancient sharks swam the seas during the Permian period. |
phases of matter Matter can exist in four phases (solid, liquid, gas, and plasma) and a few other extreme phases, like critical fluids and degenerate gases. The phase diagram of water (above) shows its phase at various temperatures and pressures. |
pillow lava Pillow lava is lava that cools under the sea, with an interconnected, sack-like form. |
pipe A pipe is a vertical passageway that runs through the Earth's crust under a volcano. Pipes are formed as magma (molten rock) travels upward through the crust. Pipes are often filled with breccia and other rock debris. |
plates The crust of the Earth is broken into plates. The plates are enormous chunks of rock that float atop the soft mantle. The plates are moving at a speed that has been estimated at 1 to 10 cm per year. Oceanic plates (those that are under the ocean) are thinner and denser than continental plates. |
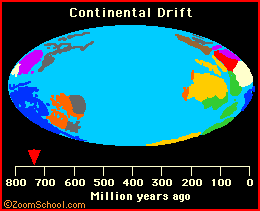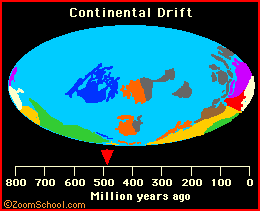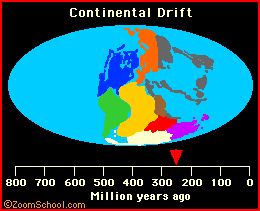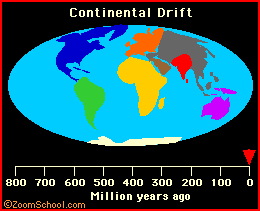 plate tectonics Plate tectonics is the now-established theory that chunks of the Earth's crust (plates) float on the surface and change both position and size over time. |
Precambrian The Precambrian is the time 540 before the Cambrian period (before million years ago). It is the time from when the Earth formed until simple life-forms evolved. |
 precipitation Precipitation is rain, sleet, hail, snow, or other condensation products falling from the atmosphere. Precipitation on Earth is is key in the water cycle. |
Volcano Info |
Volcano |
Volcano Activities and Printouts |
|
| Types of Volcanoes | The Ring of Fire | ||
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z |
Enchanted Learning®
Over 35,000 Web Pages
Sample Pages for Prospective Subscribers, or click below
|
Overview of Site What's New Enchanted Learning Home Monthly Activity Calendar Books to Print Site Index K-3 Crafts K-3 Themes Little Explorers Picture dictionary PreK/K Activities Rebus Rhymes Stories Writing Cloze Activities Essay Topics Newspaper Writing Activities Parts of Speech Fiction The Test of Time
|
Biology Animal Printouts Biology Label Printouts Biomes Birds Butterflies Dinosaurs Food Chain Human Anatomy Mammals Plants Rainforests Sharks Whales Physical Sciences: K-12 Astronomy The Earth Geology Hurricanes Landforms Oceans Tsunami Volcano |
Languages Dutch French German Italian Japanese (Romaji) Portuguese Spanish Swedish Geography/History Explorers Flags Geography Inventors US History Other Topics Art and Artists Calendars College Finder Crafts Graphic Organizers Label Me! Printouts Math Music Word Wheels |
Click to read our Privacy Policy
| Search the Enchanted Learning website for: |